How to Draw a Scenic Ground Plan
Drafting
Mechanical drawings are extremely important in technical theater. Drawings can exist fabricated by hand or with a figurer.
- Hand drafting involves the use of drafting equipment such as the T-Foursquare, triangles, a compass, and templates.
- Computer drafting requires a computer with drafting software and a printer or plotter. The Shop's computer lab is available for only such a job.
Drafting involves cartoon the object y'all want to stand for in scale. To scale a drawing means to choose a specified increase to represent a measured foot.
Multiple 2-dimensional views are used to fully draw the 3-dimensional environment of the stage.
- The Ground Plan shows a peak view and
- Sectional Cartoon provides a side view.
- Elevations are front views used by the designers and technicians to build scenery, props, article of furniture, and practicals.
- The Light Plot is used equally an accurate scaled "road map" of the Lighting Design.
.
Models and Renderings
Scale models are the best way for designers to develop and communicate their Scenic ideas.
Renderings are adept for showing mood and lighting furnishings
The Scale Rule
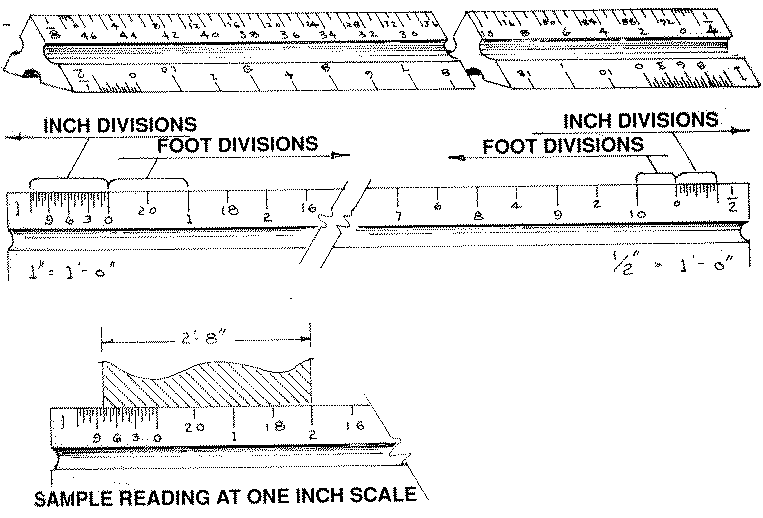
The calibration for most theater drawings is one/ii" = one'-0" though i/4 and 3/eight inch calibration are also used. 1/two inch scale is pocket-size enough to allow placement of many breathtaking units on a manageable size canvass of paper, still large plenty to specify almost detail.
Basis Plan
The Ground Plan is normally thought of every bit a bird's heart view of the stage. It aids the designer in developing the scenic blueprint. It is also used by the director for establishing the period of the action. For the lighting designer it is a mandatory instument for planning the lights. And for the phase technician information technology is invaluable in determining the placemnt of the scenery.
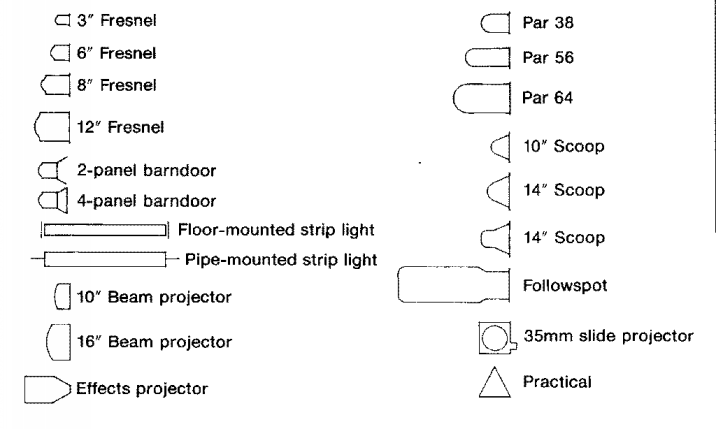
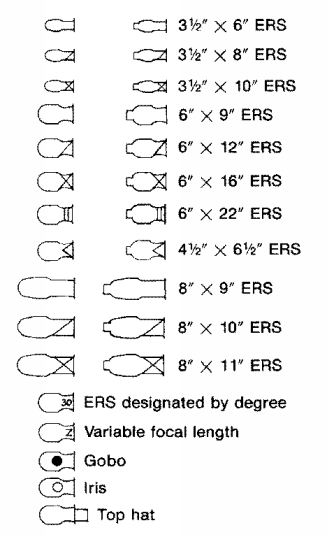
 Common symbols used in Groundplans:
Common symbols used in Groundplans:
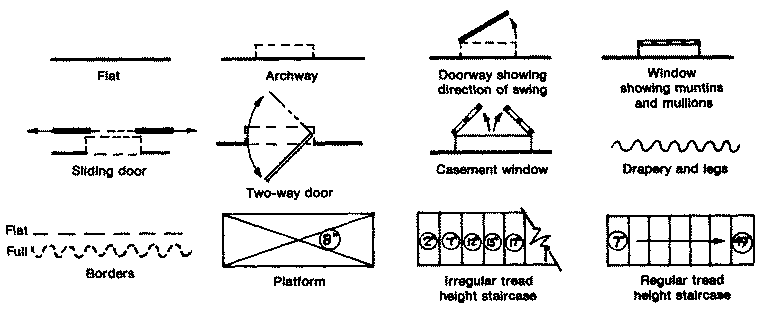
USITT Scene Design and Technical Product Graphic Standards
Sectional Drawings
The Section is a vertical dissected view of the unabridged theater, including the audition seating. The cut airplane for this view is the center line. The "cut" goes through all scenery on the stage and all scenery that is overhead, including the masking. It likewise shows the location of all lighting positions, both in the house and onstage.

Elevations
Elevations prove either the front, back, or side of a particular portion of the Footing Programme and "drag" information technology into a straight on, flattened out, full confront, no perspective view of that part of the set. It should contain all the structural information needed to build that piece of scenery and all of the practical or painted detail (moldings, trims, windows, etc.).

Light Plot
The Light Plot is a drawing indicating the placement of the lighting equipment in the theatre. The master purpose is to depict, in calibration, the verbal location of all lighting instruments used in a production. It should evidence the location of the scenery in relation to the physical structure of the theatre. Information about musical instrument type, color, and control is indicated. The plot also includes a fable describing each of the symbols used on the plot every bit well equally a championship block that details the pertinent information about the production.
Recommended Practise for Theatrical Lighting Pattern Practice
 USITT recommended lighting symbols
USITT recommended lighting symbols
All Performing Arts Groups using Annenberg Theaters, Atomic number 26 Gate Theater, Houston Hall Auditorium, or Irvine Auditorium will be expected to provide very specific descriptions of their lighting needs. This is done with the Low-cal Plot, the scaled drawing showing the placement and use of every lite needed for a product. The Lite Plot is typically drawn by the Lighting Designer. Many of the theaters take Standard Business firm Plots that provide for full general lighting for groups without experienced Lighting Designers or for productions with simply basic lighting requirements.
All Light Plots need to exist seen first by Peter Whinnery and and so past Brian Grace-Duff (for Annenberg Theaters and Irvine) or Dave Kerr (for Fe Gate and Houston Hall) for blessing at least 2 weeks prior to your show'southward load-in. These three can also answer questions about inventory and procedures. Seek them out early on!
Estimator Aided Design (CAD)
The Performing Arts Shop suports a small computer graphics lab. Cadd software used in the lab includes: AutoCad, Bricscad, Sketch-Up and VectorWorks. Bricscad is too available on the workstations in the Platt Pupil Performing Arts House.
These programs tin be used to produce plans, sections, elevations and calorie-free plots. Depending on the skill and experience of the user and the complication of what is being fatigued information technology may or may not have longer to draft on the figurer than by hand. Estimator drafting reduces the fourth dimension needed to make corrections or changes to a drawing. The computer tin can also draw objects in three dimensions, and show them from different views. This can be used in design visualization and as a manner to create plans, sections, and elevations from the same drawing ojects.
Information technology is debatable that learning to draft by hand is a ameliorate mode to acquire the bones principals than learning on the computer. You will detect youself in a situation where you lot take to draft something and either you don't accept access to a computer or you don't know the software on the estimator. Therefore yous still need to exist able to read an architect's rule, operate a T-square and triangle, draw a straight line, and perform the other drafting skills.
Breathtaking Models
Models are well-nigh useful in visualizing the composition of the breathtaking design and its relationship with the theater space and audience. Most often constucted in one/2 in scale the model is a miniature version of the finished set up.

Rendering
A typical rendering of the scenic design shows the setting every bit it appears to the audition. Most likely, it will represent an important or dramatic scene from the production. The designer renders it to indicate how the setting volition look under phase lighting, consummate with mood, atmosphere, and depth.
Renderings can be washed in all sorts of painting and drawing media, including: watercolors, acrylics, pastels, charcoal, Bharat ink, colored pencils, chalk, or even oil paints. The designer selects the medium in terms of what works best for him/her and what will give the desired results. Oftentimes it is a combination of many media.

Renderings can also be washed with the aid of a computer. At that place are many drawing and painting programs on the market including: PhotoShop, Painter, Poser, Gimp, and Strata StudioVision. Very interesting results can also be had by combining computer output with hand drawing and painting. For example a wire frame image tin can be printed from a drafting progam and and then hand colored. Going to other way - one can scan hand fatigued images to be manipulated with other images in a programme like Photoshop or Gimp.

Source: https://www.dolphin.upenn.edu/pacshop/graphics.html
0 Response to "How to Draw a Scenic Ground Plan"
Postar um comentário